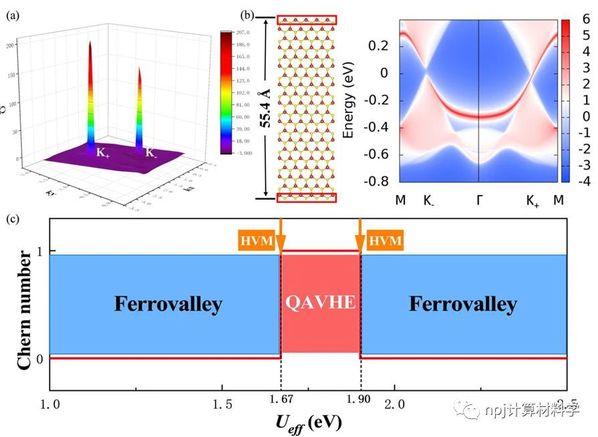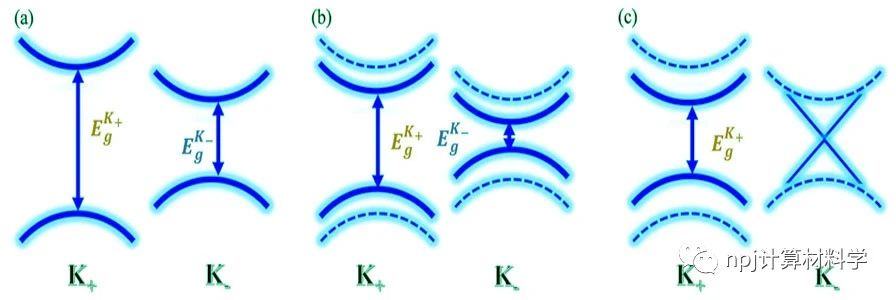
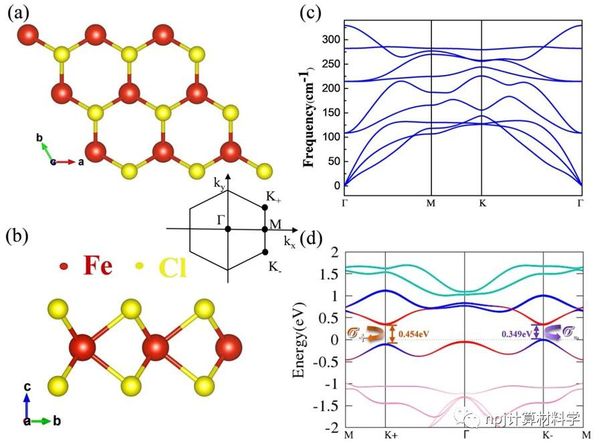
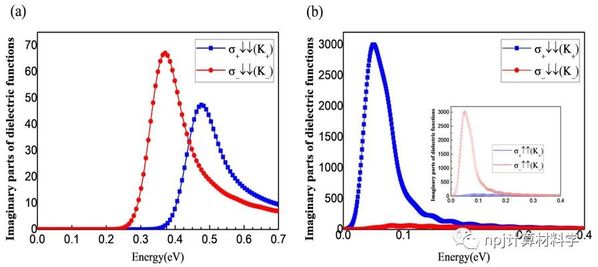
二维材料的出现推动了基于能谷自由度的谷电子学研究,其发展道路紧跟专注于自旋自由度的自旋电子学。类似于自旋电子学中的重要概念---半金属,即体系中一个自旋通道处于导电状态,而另一个自旋通道处于绝缘状态,此项工作的提出扩充了谷电子家族成员,提出了半谷金属的概念,即在一个能谷处呈现金属态,而在另一不等价能谷处依旧保持半导体特性。本工作由华东师范大学极化材料与器件教育部重点实验室的段纯刚教授(本刊副主编)团队和南京大学物理系万贤纲教授合作完成,他们通过双带k·p模型证明了实现铁谷新成员半谷金属态的可能性,并从贝里曲率的解析解中得知该系统可以从拓扑平庸态进入具有非零陈数的拓扑非平庸态。而这一拓扑状态提供了保留有能谷自由度的量子反常谷霍尔效应,确保了谷电子材料中的低耗散高性能的电子传输。进一步地,该团队通过第一性原理计算在铁谷材料H-FeCl2单层中,引入有效的交换关联U参数来描述过渡金属Fe-3d电子的强相关效应,成功实现了半谷金属态和拓扑非平庸态。同时,在半谷金属态时,仅左旋圆偏振光可以被吸收,这表明半谷金属系统获得了100%的谷极化。进一步分析发现,在两个半谷金属态之间施加U效应(或等效磁场)的过程中,两能谷处的能带成分交换不同步,导致系统从拓扑平庸态变为具有非零陈数的拓扑非平庸状态,在这种H-FeCl2单层中得到了具有谷自由度的量子反常谷霍尔效应。这些新概念极大地丰富了对谷电子学的理解,从而可加速其在信息处理和光电领域的应用。
Editorial Summary
The emergence of two-dimensional materials has promoted the research of valleytronics based on energy valley degrees of freedom. The development of valleytronics follows exactly that of spintronics which depends on spin degree of freedom. Similar to the important concept in spintronics, half-metal, in which one of the spin channel is in a conducting state, while another spin channel is in the insulation state, this work introduces a new member to the family of valleytronic materials, i.e. half-valley metal (HVM), which keeps metallic state in a valley and semiconductor state in another in equivalent valley.
This work is proposed by Prof. Chun-Gang Duan (an Associate Editor-in-Chief of npj Computational Materials) and his team in Key Laboratory of Polar Materials and Devices, Ministry of Education, East China Normal University, in collaboration with Prof. Xiangang Wan of Nanjing university. By means of the two-band k·p model they prove the possibility of forming the HVM state, and from the analytical solution of the berry curvature, it can be seen that the system could transform from topological trivial state into the nontrivial state with nonzero Chern number. The topological state provides the quantum anomalous valley Hall effect which preserves the energy valley degree of freedom and further ensures the low dissipation and high performance electron transport in valleytronic materials. Furthermore, the team introduces effective exchange associated U parameter to describe the strong correlation effect of transition metal Fe-3d electrons through first-principles calculation in ferrovalley material H-FeCl2 monolayers, and successfully realizes the HVM state and topological state. At the same time, only left-circularly polarized light can be absorbed in the HVM state, which indicates that it achieves 100% valley polarization. According to the analysis, in the process of applying U effect between two HVM states, the exchange of energy band components at the two energy valleys is not simultaneous, resulting in the system changing from a topological trivial state to a topological nontrivial state with non-zero Chern number. Consequently, in this H-FeCl2 monolayers, quantum anomalous valley hall effect with valley property is obtained.
These new concepts greatly enrich the understanding of valleytronics, thus accelerating its application in the field of information processing and optoelectronics. This article was recently published in npj Computational Materials 6: 129 (2020).
原文Abstract及其翻译
Concepts of the half-valley-metal and quantum anomalous valley Hall effect (半谷金属及量子反常谷霍尔效应)
He Hu, Wen-Yi Tong, Yu-Hao Shen, Xiangang Wan & Chun-Gang Duan
Abstract Valley, the energy extrema in the electronic band structure at momentum space, is regarded as a new degree of freedom of electrons, in addition to charge and spin. The studies focused on valley degree of freedom now form an emerging field of condensed-matter physics, i.e., valleytronics, whose development is exactly following that of spintronics, which focuses on the spin degree of freedom. Here, in analogy to half-metals in spintronics where one spin channel is conducting, whereas the other is insulating, we propose the concept of half-valley metal, in which conduction electrons are intrinsically 100% valley polarized, as well as 100% spin polarized even when spin–orbit interactions are considered. Combining first-principle calculations with a two-band k·p model, the physical mechanism to form the half-valley metal is illuminated. Taking the ferrovalley H-FeCl2 monolayer with strong exchange interaction as an example, we find that the strong electron correlation effect can induce the ferrovalley to half-valley-metal transition. Due to the valley-dependent optical selection rules, such a system could be transparent to, e.g., left-circularly polarized light, yet the right-circularly polarized light will be reflected, which can in turn be used as a crucial method to detect the half-valley-metal state. Interestingly, with the increase of the correlation effect, the system becomes insulating again with all valleys following the same optical selection rule. We confirm that in this specific case, the valence bands, which consist of single spin, possess nonzero Chern number and consequently an intrinsic quantum anomalous valley Hall effect emerges. Our findings open an appealing route toward functional 2D materials design of valleytronics.
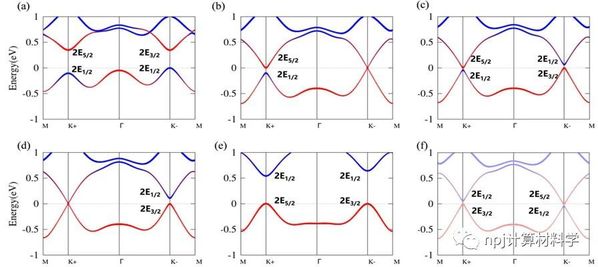
摘要 能谷是电子能带结构在动量空间中的能量极值点,被认为是电子除电荷和自旋之外的一个新的自由度。以谷自由度为核心的研究现在形成了凝聚态物理学的一个新兴领域,即谷电子学,它的发展与以自旋自由度为核心的自旋电子学的发展非常一致。这里,类比于自旋电子学中的半金属(即体系中一个自旋通道导电,而另一个自旋通道绝缘体,所以传导电子自旋极化率为100%),我们提出了半谷金属的概念,其中传导电子本质上是100%谷极化的,同时也是100%自旋极化的,即使考虑自旋轨道相互作用时也是如此。我们首先将第一性原理计算与双带k×p模型相结合,阐明了半谷金属态形成的物理机制。以具有强交换关联作用的铁谷H-FeCl2单层为例,我们发现电子强关联效应(或者外加磁场)可诱导谷极化状态向半谷金属态过渡。考虑到能谷相关的光学选择定则,在半谷金属状态时,系统将对特定旋性的光(例如左旋圆偏振光)透明,但是另一旋性的光如右旋圆偏振光将被反射,这一特性同时可以用作检测半谷金属态。另外,我们发现在所获得的半谷金属状态下,传导电子的能谷表现出狄拉克锥状线性能量色散关系。更有趣的是,随着交换关联作用的增大,闭合的能谷将再次拥有带隙,此时所有能谷都遵循相同的光学选择规则,即对应同一旋性的圆偏光吸收。在这种特定情况下,由单一自旋组成的价带顶具有非零的陈数,因此出现了本征量子反常谷霍尔效应。半谷金属以及本征量子反常谷霍尔效应概念的提出为谷电子学与光学,自旋电子学以及拓扑等领域的交叉研究提供了新颖的物理理念,也为功能性二维材料设计开辟了一条引人入胜的途径。